Wrapper Class
기본형 값들을 객체로 변환하여 작업을 수행해야 할 때 사용되는 클래스
- 매개변수로 객체를 요구할 때, 기본형 값이 아닌 객체로 저장해야할 때, 객체 간의 비교가 필요할 때 등등
- 기본형(primitive type) 변수를 객체로 다룰 수 있게 해준다.
| 기본형 | 래퍼클래스 | 생성자 | 예 |
|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | Boolean | Boolean(boolean value) Boolean(String s) | Boolean b = new Boolean(true); Boolean b2 = new Boolean(“true”); |
| char | Character | Character(char value) | Character c = new Character(‘a’); |
| byte | Byte | Byte(byte value) Byte(String s) | Byte b = new Byte(10); Byte b2 = new Byte(“10”); |
| short | Short | Short(short value) Short(String s) | Short s = new Short(10); Short s2 = new Short(“10”); |
| int | Integer | Integer(int value) Integer(String s) | Integer i = new Integer(100); Integer i2 = new Integer(“100”); |
| long | Long | Long(long value) Long(String s) | Long l = new Long(100); Long l2 = new Long(“100”); |
| float | Float | Float(double value) Float(float value) Float(String s) | Float f = new Float(1.0); Float f2 = new Float(1.0f); Float f3 = new Float(“1.0f”); |
| double | Double | Double(double value) Double(String s) | Double d = new Double(1.0); Double d2 = new Double(“1.0”); |
- char, int형을 제외한 나머지는 자료형의 첫 글자를 대문자로 한 것이 각 래퍼 클래스의 이름이다.
- 생성자는 매개변수로 문자열이나 각 자료형의 값들을 인자로 받는다.
- 생성자의 매개변수로 각 자료형에 맞는 문자열을 사용해야 한다. (자료형에 맞지 않는 문자열을 넘길 경우 NumberFormatException이 발생한다. 예
new Integer("1.0");)
- 생성자의 매개변수로 각 자료형에 맞는 문자열을 사용해야 한다. (자료형에 맞지 않는 문자열을 넘길 경우 NumberFormatException이 발생한다. 예
Number 클래스
추상클래스이며, 내부적으로 숫자를 멤버변수로 갖는 래퍼 클래스들의 조상이다.
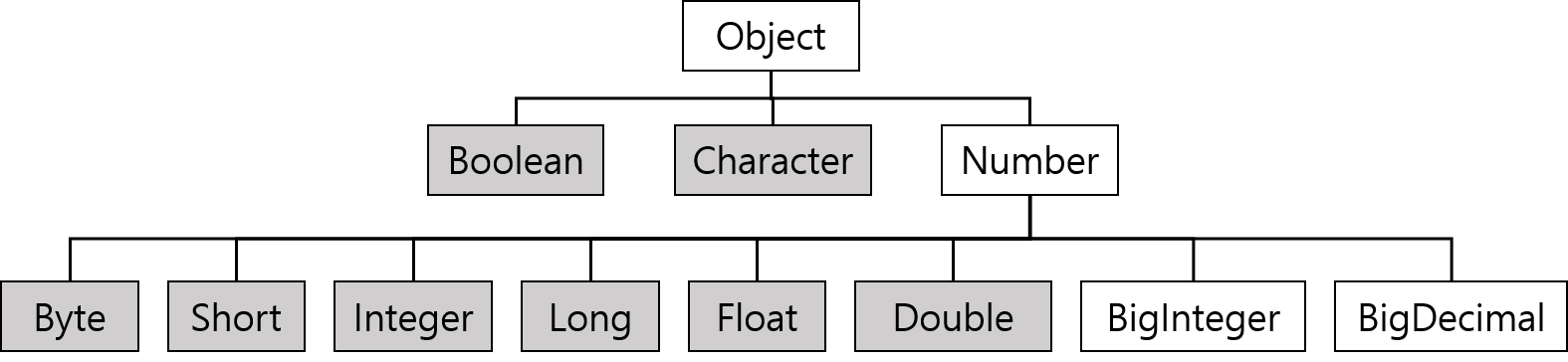
- BigInteger은 long으로도 다룰 수 없는 큰 범위의 정수를, BigDecimal은 double로도 다룰 수 없는 큰 범위의 부동 소수점수를 처리하기 위한 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public abstract class Number implements java.io.Serializable {
public abstract int intValue();
public abstract long longValue();
public abstract float floatValue();
public abstract double doubleValue();
public byte byteValue() {
return (byte)intValue();
}
public short shortValue() {
return (short)intValue();
}
}
문자열 → 숫자
- 문자열 → 기본형(primitive) :
타입.parse타입(String s) - 문자열 → 래퍼 클래스 :
타입.valueOf()
| 문자열 → 기본형 | 문자열 → 래퍼 클래스 |
|---|---|
| byte b = Byte.parseByte(“100”); short s = Short.parseShort(“100”); int i = Integer.parseInt(“100”); long l = Long.parseLong(“100”); float f = Float.parseFloat(“3.14”); double d = Double.parseDouble(“3.14”); | Byte b = Byte.valueOf(“100”); Short s = Short.valueOf(“100”); Integer i = Integer.valueOf(“100”); Long l = Long.valueOf(“100”); Float f = Float.valueOf(“3.14”); Double d = Double.valueOf(“3.14”); |
JDK 1.5부터 오토박싱 기능 때문에 반환값이 기본형일 때와 래퍼클래스일 때의 차이가 없어졌다.
- 그래서 구별없이 valueOf()를 사용해도 괜찮은 방법이다. (성능은 valueOf가 더 느림)
10진수가 아닌 다른 진법(radix)의 숫자일 때도 변환 가능하다. (진법 생략 시 10진수로 간주)
1 2 3
// value는 10진수로 변환할 숫자, radix는 진법 static int parseInt(String value, int radix) static Integer valueOf(String value, int radix)
1 2 3 4
int i2 = Integer.parseInt("100", 2); // 100(2) -> 4 int i8 = Integer.parseInt("100", 8); // 100(8) -> 64 int i16 = Integer.parseInt("FF", 16); // FF(16) -> 255 //int j16 = Integer.parseInt("FF"); // NumberFormatException 발생(10진수로 간주)
Autoboxing & unboxing
Autoboxing(오토박싱) : 기본형 값을 래퍼클래스의 객체로 자동 변환해주는 것
Unboxing(언박싱) : 래퍼클래스의 객체를 기본형 값으로 자동 변환해주는 것
1
2
3
4
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(10); // 오토박싱. 10 → new Integer(10)
int value = list.get(0); // 언박싱. new Integer(10) → 10
JDK 1.5부터 가능하다.
컴파일러가 기본형과 참조형 간에 형변환이 필요할 때 자동적으로 코드를 추가한다.
자바의 원칙이 바뀐 것이 아니라 개발자가 간략하게 쓴 구문을 컴파일러가 원래의 구문으로 변경해주는 것뿐이다.
컴파일 전의 코드 컴파일 후의 코드 int i = 10;
Integer intg = (Integer)i;
Object obj = (Object)i;
Long lng = 100L;int i = 10;
Integer intg = Integer.valueOf(i);
Object obj = (Object)Integer.valueOf(i);
Long lng = new Long(100L);
출처📎
- 자바의 정석
